【注意】最后更新于 June 17, 2023,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
1.介绍
高级加密标准(英语:Advanced Encryption Standard,缩写:AES),又称Rijndael加密法(荷兰语发音:[ˈrɛindaːl],音似英文的“Rhine doll”),是美国联邦政府采用的一种区块加密标准。这个标准用来替代原先的DES,已经被多方分析且广为全世界所使用。经过五年的甄选流程,高级加密标准由美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)于2001年11月26日发布于FIPS PUB 197,并在2002年5月26日成为有效的标准。现在,高级加密标准已然成为对称密钥加密中最流行的算法之一。
该算法为比利时密码学家Joan Daemen和Vincent Rijmen所设计,结合两位作者的名字,以Rijndael为名投稿高级加密标准的甄选流程。
2. 电码本模式(ECB)
2.1 加密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
// 加密
func AesEncryptByECB(data, key string) string {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// 密钥和待加密数据转成[]byte
originByte := []byte(data)
keyByte := []byte(key)
// 创建密码组,长度只能是16、24、32字节
block, _ := aes.NewCipher(keyByte)
// 获取密钥长度
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 补码
originByte = PKCS7Padding(originByte, blockSize)
// 创建保存加密变量
encryptResult := make([]byte, len(originByte))
// CEB是把整个明文分成若干段相同的小段,然后对每一小段进行加密
for bs, be := 0, blockSize; bs < len(originByte); bs, be = bs+blockSize, be+blockSize {
block.Encrypt(encryptResult[bs:be], originByte[bs:be])
}
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(encryptResult)
}
// 补码
func PKCS7Padding(originByte []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
// 计算补码长度
padding := blockSize - len(originByte)%blockSize
// 生成补码
padText := bytes.Repeat([]byte{byte(padding)}, padding)
// 追加补码
return append(originByte, padText...)
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
// 加密
func TestECBEncrypt(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
data := "hello word"
s := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByECB(data, key)
fmt.Printf("加密密钥: %v \n", key)
fmt.Printf("加密数据: %v \n", data)
fmt.Printf("加密结果: %v \n", s)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestECBEncrypt
加密密钥: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
加密数据: hello word
加密结果: mMAsLF/fPBfUrP0mPqZm1w==
--- PASS: TestECBEncrypt (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
c.第三方加密验证
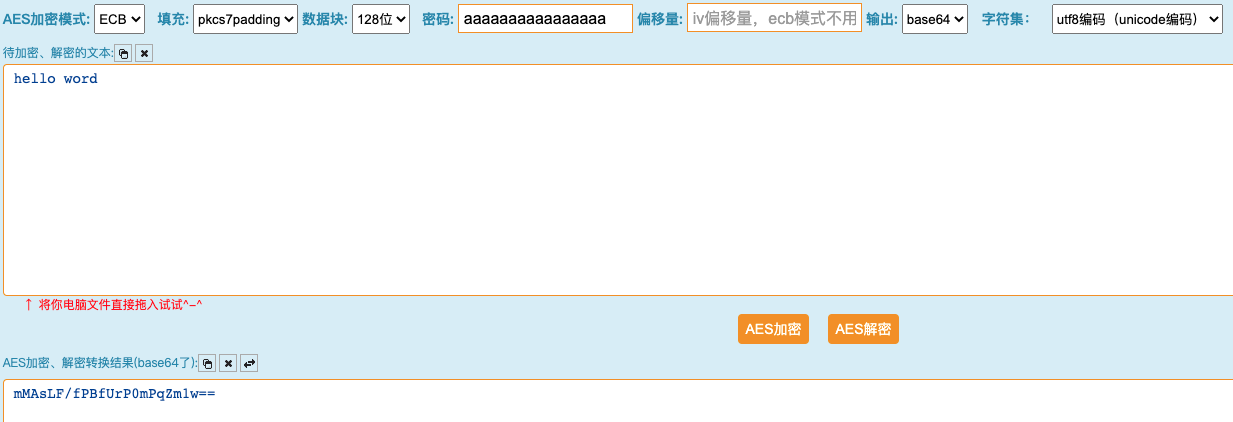
2.2 解密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
// 解密
func AesDecryptByECB(data, key string) string {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// 反解密码base64
originByte, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(data)
// 密钥和待加密数据转成[]byte
keyByte := []byte(key)
// 创建密码组,长度只能是16、24、32字节
block, _ := aes.NewCipher(keyByte)
// 获取密钥长度
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 创建保存解密变量
decrypted := make([]byte, len(originByte))
for bs, be := 0, blockSize; bs < len(originByte); bs, be = bs+blockSize, be+blockSize {
block.Decrypt(decrypted[bs:be], originByte[bs:be])
}
// 解码
return string(PKCS7UNPadding(decrypted))
}
// 解码
func PKCS7UNPadding(originDataByte []byte) []byte {
length := len(originDataByte)
unpadding := int(originDataByte[length-1])
return originDataByte[:(length-unpadding)]
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
// 解密
func TestECBDecrypt(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
data := "mMAsLF/fPBfUrP0mPqZm1w=="
s := cryptopkg.AesDecryptByECB(data, key)
fmt.Printf("解密密钥: %v \n", key)
fmt.Printf("解密数据: %v \n", data)
fmt.Printf("解密结果: %v \n", s)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestECBDecrypt
解密密钥: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
解密数据: mMAsLF/fPBfUrP0mPqZm1w==
解密结果: hello word
--- PASS: TestECBDecrypt (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
3. 密码分组链模式(CBC)
3.1 加密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// AES加密
func AesEncryptByCBC(str, key string) string {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// 待加密字符串转成byte
originDataByte := []byte(str)
// 秘钥转成[]byte
keyByte := []byte(key)
// 创建一个cipher.Block接口。参数key为密钥,长度只能是16、24、32字节
block, _ := aes.NewCipher(keyByte)
// 获取秘钥长度
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 补码填充
originDataByte = PKCS7Padding(originDataByte, blockSize)
// 选用加密模式
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCEncrypter(block, keyByte[:blockSize])
// 创建数组,存储加密结果
encrypted := make([]byte, len(originDataByte))
// 加密
blockMode.CryptBlocks(encrypted, originDataByte)
// []byte转成base64
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(encrypted)
}
// 补码
func PKCS7Padding(originByte []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
// 计算补码长度
padding := blockSize - len(originByte)%blockSize
// 生成补码
padText := bytes.Repeat([]byte{byte(padding)}, padding)
// 追加补码
return append(originByte, padText...)
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
// AES加密
func TestAesEncryptByCBC(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
fmt.Printf("key: %v 长度: %d \n", key, len(key))
text := "abc"
fmt.Printf("带加密文案: %v \n", text)
encrypt := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByCBC(text, key)
fmt.Printf("加密结果: %v \n", encrypt)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesEncryptByCBC
key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa 长度: 16
带加密文案: abc
加密结果: rMX6r9x+PnTOhfgDH4jjXg==
--- PASS: TestAesEncryptByCBC (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
c.第三方验证

3.2 解密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
// 解密
func AesDecryptByCBC(encrypted,key string) string {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// encrypted密文反解base64
decodeString, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(encrypted)
// key 转[]byte
keyByte := []byte(key)
// 创建一个cipher.Block接口。参数key为密钥,长度只能是16、24、32字节
block, _ := aes.NewCipher(keyByte)
// 获取秘钥块的长度
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 选择加密模式
blockMode := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, keyByte[:blockSize])
// 创建数组,存储解密结果
decodeResult := make([]byte, blockSize)
// 解密
blockMode.CryptBlocks(decodeResult,decodeString)
// 解码
padding := PKCS7UNPadding(decodeResult)
return string(padding)
}
// 解码
func PKCS7UNPadding(originDataByte []byte) []byte {
length := len(originDataByte)
unpadding := int(originDataByte[length-1])
return originDataByte[:(length-unpadding)]
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
// AES解密
func TestAesDecryptByCBC(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
fmt.Printf("key: %v 长度: %d \n", key, len(key))
text := "rMX6r9x+PnTOhfgDH4jjXg=="
fmt.Printf("待解密文案: %v \n", text)
decrypt := cryptopkg.AesDecryptByCBC(text, key)
fmt.Printf("解密结果: %v \n", decrypt)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesDecryptByCBC
key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa 长度: 16
待解密文案: rMX6r9x+PnTOhfgDH4jjXg==
解密结果: abc
--- PASS: TestAesDecryptByCBC (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
4. 计算器模式(CTR)
4.1 加密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
// 加密,分别返回 hex格式和base64 结果
func AesEncryptByCTR(data, key string) (string,string) {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// 转成byte
dataByte := []byte(data)
keyByte := []byte(key)
// 创建block
block, err := aes.NewCipher(keyByte)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewCipher error:%s",err))
}
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 创建偏移量iv,取秘钥前16个字符
iv := []byte(key[:blockSize])
// 补码
padding := PKCS7Padding(dataByte, blockSize)
// 加密模式
stream := cipher.NewCTR(block, iv)
// 定义保存结果变量
out := make([]byte,len(padding))
stream.XORKeyStream(out,padding)
// 处理加密结果
hexRes := fmt.Sprintf("%x",out)
base64Res := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(out)
return hexRes,base64Res
}
// 补码
func PKCS7Padding(originByte []byte, blockSize int) []byte {
// 计算补码长度
padding := blockSize - len(originByte)%blockSize
// 生成补码
padText := bytes.Repeat([]byte{byte(padding)}, padding)
// 追加补码
return append(originByte, padText...)
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
// 测试AES-CTR加密
func TestAesEncryptByCTR(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
data := "hello word"
hex, base64 := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByCTR(data, key)
fmt.Printf("加密key: %v \n", key)
fmt.Printf("加密key长度: %v \n", len(key))
fmt.Printf("加密数据: %v \n", data)
fmt.Printf("加密结果(hex): %v \n", hex)
fmt.Printf("加密结果(base64): %v \n", base64)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesEncryptByCTR
加密key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
加密key长度: 16
加密数据: hello word
加密结果(hex): 39edaa2b2402fbd2a026ef1458b81b55
加密结果(base64): Oe2qKyQC+9KgJu8UWLgbVQ==
--- PASS: TestAesEncryptByCTR (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
c.第三方加密验证
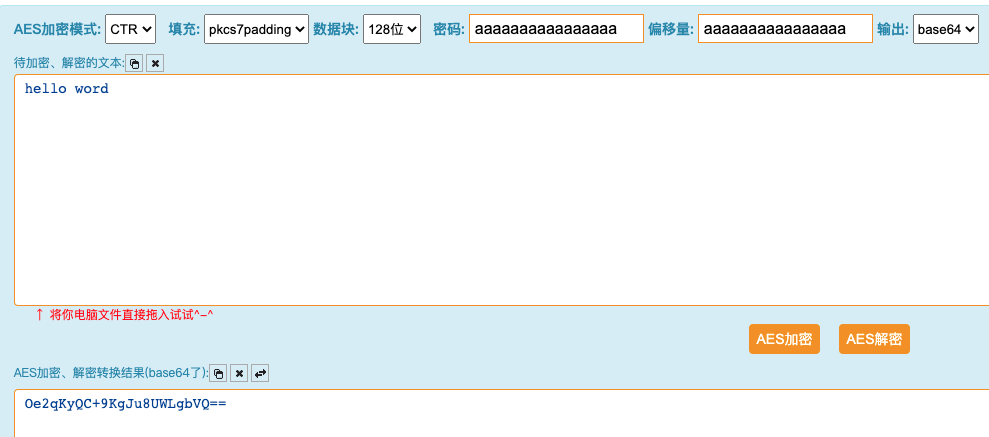
4.2 解密
a.代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
// 解密
func AesDecryptByCTR(dataBase64,key string) string {
// 判断key长度
keyLenMap := map[int]struct{}{16: {}, 24: {}, 32: {}}
if _,ok := keyLenMap[len(key)]; !ok {
panic("key长度必须是 16、24、32 其中一个")
}
// dataBase64转成[]byte
decodeStringByte, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(dataBase64)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("base64 DecodeString error: %s",err))
}
// 创建block
block, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(key))
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewCipher error: %s",err))
}
blockSize := block.BlockSize()
// 创建偏移量iv,取秘钥前16个字符
iv := []byte(key[:blockSize])
// 创建Stream
stream := cipher.NewCTR(block, iv)
// 声明变量
out := make([]byte,len(decodeStringByte))
// 解密
stream.XORKeyStream(out,decodeStringByte)
// 解密加密结果并返回
return string(PKCS7UNPadding(out))
}
|
b.测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
// 测试AES-CTR解密
func TestAesDecryptByCTR(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
data := "Oe2qKyQC+9KgJu8UWLgbVQ=="
res := cryptopkg.AesDecryptByCTR(data, key)
fmt.Printf("解密key: %v \n", key)
fmt.Printf("解密数据: %v \n", data)
fmt.Printf("解密结果: %v \n", res)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesDecryptByCTR
解密key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
解密数据: Oe2qKyQC+9KgJu8UWLgbVQ==
解密结果: hello word
--- PASS: TestAesDecryptByCTR (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|
5. CFB、OFB
和CTR模式一样,只需要修改加密模式即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// CFB
...
stream := cipher.NewCFBDecrypter(block, iv)
...
// OFB
...
stream := cipher.NewOFB(block, iv)
...
|
不理解的点: 在学习使用中,发现CFB/OFB/CTR 在加密很短的字符串时,发现加密结果一致。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
func TestAesEncryptByOFB(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a", 16)
data := "123"
_, base64 := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByOFB(data, key)
_, base642 := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByCTR(data, key)
_, base643 := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByCFB(data, key)
fmt.Printf("加密key: %v \n", key)
fmt.Printf("加密key长度: %v \n", len(key))
fmt.Printf("加密数据: %v \n", data)
fmt.Printf("加密结果(OFB): %v \n", base64)
fmt.Printf("加密结果(CTR): %v \n", base642)
fmt.Printf("加密结果(CFB): %v \n", base643)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesEncrypt
加密key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
加密key长度: 16
加密数据: 123
加密结果(OFB): YLr1SkYvgbDfT+QfU7MQXg==
加密结果(CTR): YLr1SkYvgbDfT+QfU7MQXg==
加密结果(CFB): YLr1SkYvgbDfT+QfU7MQXg==
--- PASS: TestAesEncrypt (0.00s)
PASS
|
6.AES-GCM
GCM 全称为Galois/Counter Mode,可以看出 G 是指 GMAC,C 是指 CTR。它在 CTR 加密的基础上增加 GMAC 的特性,解决了 CTR 不能对加密消息进行完整性校验的问题。
6.1 加密
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// 加密(GCM 不需要补码)
func AesEncryptByGCM(data, key string) string {
block, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(key))
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewCipher error:%s", err))
}
gcm, err := cipher.NewGCM(block)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewGCM error:%s", err))
}
// 生成随机因子(这里固定取密钥指定位数)
//nonce := make([]byte, gcm.NonceSize())
//if _,err := io.ReadFull(rand.Reader,nonce); err != nil {
// panic(fmt.Sprintf("make rand nonce error:%s", err))
//}
nonceStr := key[:gcm.NonceSize()]
nonce := []byte(nonceStr)
fmt.Printf("nonceStr = %v \n", nonceStr)
seal := gcm.Seal(nonce, nonce, []byte(data), nil)
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(seal)
}
|
6.2 解密
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
// 解密(GCM 不需要解码)
func AesDecryptByGCM(data, key string) string {
// 反解base64
dataByte,err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(data)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("base64 DecodeString error:%s", err))
}
block, err := aes.NewCipher([]byte(key))
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewCipher error:%s", err))
}
gcm, err := cipher.NewGCM(block)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("NewGCM error:%s", err))
}
nonceSize := gcm.NonceSize()
if len(dataByte) < nonceSize {
panic("dataByte to short")
}
nonce, ciphertext := dataByte[:nonceSize], dataByte[nonceSize:]
open, err := gcm.Open(nil, nonce, ciphertext, nil)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintf("gcm Open error:%s", err))
}
return string(open)
}
|
6.3 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
package crypto
import (
"shershon1991/go-tools/app/cryptopkg"
"fmt"
"strings"
"testing"
)
func TestAesGCM(t *testing.T) {
key := strings.Repeat("a",16)
data := "hello word!"
// 加密
gcm := cryptopkg.AesEncryptByGCM(data, key)
fmt.Printf("密钥key: %s \n",key)
fmt.Printf("加密数据: %s \n",data)
fmt.Printf("加密结果: %s \n",gcm)
// 解密
byGCM := cryptopkg.AesDecryptByGCM(gcm, key)
fmt.Printf("解密结果: %s \n",byGCM)
}
/** 输出
=== RUN TestAesGCM
nonceStr = aaaaaaaaaaaa
密钥key: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
加密数据: hello word!
加密结果: YWFhYWFhYWFhYWFhhi5dsHDfOdUFfno08BMWWI4iESBd0CF6zE9C
解密结果: hello word!
--- PASS: TestAesGCM (0.00s)
PASS
*/
|


