【注意】最后更新于 June 18, 2023,文中内容可能已过时,请谨慎使用。
1. 介绍
Go语言中的pprof指对于指标或特征的分析(Profiling),通过分析不仅可以查找到程序中的错误(内存泄漏、race冲突、协程泄漏),也能对程序进行优化(例如CPU利用率不足)。
由于Go语言运行时的指标不对外暴露,因此有标准库net/http/pprof和runtime/pprof用于与外界交互。其中net/http/pprof提供了一种通过http访问的便利方式,用于用户调试和获取样本特征数据。
对特征文件进行分析要依赖谷歌推出的分析工具pprof,该工具在Go安装时即存在。
2. 收集样本
在通过pprof进行特征分析时,需要执行两个步骤:收集样本和分析样本
pprof 采样数据主要有三种获取方式:
-
net/http/pprof: 通过 http 服务获取Profile采样文件,简单易用,适用于对应用程序的整体监控。底层也是通过 runtime/pprof 实现。
-
runtime/pprof: 手动调用runtime.StartCPUProfile或者runtime.StopCPUProfile等 API来生成和写入采样文件,灵活性更高。
-
go test: 通过 go test -cpuprofile cpu.pprof -memprofile mem.pprof生成采样文件,适用对函数进行针对性测试。其中-cpuprofile:生成CPU性能测试信息; -memprofile:生成内存占用信息;
2.1 使用net/http/pprof
1. 源码详情
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof" // 导入pprof
"strings"
"time"
)
func init() {
//开启http端口,用协程的方式监听,否则会阻塞
go func() {
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":6060", nil); err != nil {
fmt.Println("pprof err:",err)
}
}()
}
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
engine.GET("/test", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200,gin.H{
"msg":"success",
})
})
testPprofHeap()
_ = engine.Run(":8080")
}
// 模拟内存使用增加
func testPprofHeap() {
go func() {
var stringSlice []string
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second *2)
repeat := strings.Repeat("hello,world", 50000)
stringSlice = append(stringSlice,repeat)
fmt.Printf("time:%d length:%d \n",time.Now().Unix(),len(stringSlice))
}
}()
}
|
2. 访问端口

2.2 使用runtime/pprof
通过http收集样本是在实践中最常见的方式,但有时可能不太适合,例如对于一个测试程序或只跑一次的定时任务。可以调用runtime/pprof的StartCPUProfile函数,这样,在程序调用StopCPUProfile函数停止之后,即可指定特征文件保存的位置。
1. 代码详情
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package tests
import (
"os"
"runtime/pprof"
"testing"
"time"
)
func TestRuntimePProf(t *testing.T) {
// 打开文件
f, err := os.Create("../profile/out.pprof")
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("文件打开失败:%v", err)
return
}
// 调用
err = pprof.StartCPUProfile(f)
defer pprof.StopCPUProfile()
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("StartCPUProfile:%v", err)
}
// 测试单独函数
testPprof()
}
// 模拟内存使用增加
func testPprof() {
ch := make(chan bool)
go func() {
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ {
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 200)
}
ch <- true
}()
<-ch
}
|
2. 运行测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
# 运行
➜ go test runtime_pprof_test.go -v
=== RUN TestRuntimePProf
--- PASS: TestRuntimePProf (5.05s)
PASS
ok command-line-arguments 5.448s
# 查看pprof
➜ go tool pprof out.pprof
Type: cpu
Time: Nov 15, 2021 at 4:09pm (CST)
Duration: 4.06s, Total samples = 0
No samples were found with the default sample value type.
Try "sample_index" command to analyze different sample values.
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof)
|
2.3 使用go test
使用格式 go test . -x 文件
-cpuprofile: 生成CPU性能信息。-memprofile: 生成内存占用信息。-mutexprofile:生成锁争用情况。
1. 代码详情
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
package tests
import (
"strings"
"testing"
"time"
)
func TestWithPProf(t *testing.T) {
ch := make(chan bool)
go func() {
var stringSlice []string
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ {
repeat := strings.Repeat("hello,world", 50000)
stringSlice = append(stringSlice,repeat)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500)
}
ch <- true
}()
<-ch
}
|
2. 运行测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# 运行单元测试
➜ go test go_test.go -cpuprofile ../profile/cpu.pprof -memprofile ../profile/mem.pprof
# 查看内存pprof
➜ go tool pprof mem.pprof
Type: alloc_space
Time: Nov 15, 2021 at 4:22pm (CST)
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof)
|
3. 分析样本
pprof提供了很多维度的分析,若想分析某一个维度信息,可直接使用go tool pprof http://ip:port/debug/pprof/维度,进入交互式分析。
3.1 分析维度
allocs:查看过去所有内存分配的样本,访问路径为/debug/pprof/allocs。block:查看导致阻塞同步的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为/debug/pprof/block。cmdline:当前程序的命令行的完整调用路径。goroutine:查看当前所有运行的 goroutines 堆栈跟踪,访问路径为/debug/pprof/goroutine。heap:查看活动对象的内存分配情况, 访问路径为/debug/pprof/heap。mutex:查看导致互斥锁的竞争持有者的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为/debug/pprof/mutex。profile:默认进行 30s 的 CPU Profiling,得到一个分析用的 profile 文件,访问路径为/debug/pprof/profile。threadcreate:查看创建新OS线程的堆栈跟踪,访问路径为/debug/pprof/threadcreate。
最常用的4种pprof类型包括了堆分析heap、协程栈分析goroutine、CPU占用分析profile、程序运行跟踪信息trace
3.2 交互式分析
下面以堆内存(heap)分析为示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
# 进入交互命令
➜ go tool pprof http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap?debug=1
Fetching profile over HTTP from http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap?debug=1
Saved profile in /Users/liuqh/pprof/pprof.alloc_objects.alloc_space.inuse_objects.inuse_space.003.pb.gz
Type: inuse_space
Entering interactive mode (type "help" for commands, "o" for options)
(pprof) top # top 列出以fat列从大到小排序的序列
Showing nodes accounting for 11004.99kB, 100% of 11004.99kB total
Showing top 10 nodes out of 18
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
9975.41kB 90.64% 90.64% 9975.41kB 90.64% strings.(*Builder).grow
517.33kB 4.70% 95.35% 517.33kB 4.70% regexp/syntax.(*compiler).inst
512.25kB 4.65% 100% 512.25kB 4.65% regexp.onePassCopy
0 0% 100% 517.33kB 4.70% github.com/go-playground/validator/v10.init
0 0% 100% 512.25kB 4.65% github.com/go-playground/validator/v10.init.0
0 0% 100% 9975.41kB 90.64% main.testPprofHeap.func1
0 0% 100% 1029.58kB 9.36% regexp.Compile
0 0% 100% 1029.58kB 9.36% regexp.MustCompile
0 0% 100% 1029.58kB 9.36% regexp.compile
0 0% 100% 512.25kB 4.65% regexp.compileOnePass
|
1.flat|flat%|sum%|cum|cum%
针对不同的维度,展示代表的含义也有所区别,比如:当分析维度是profile时,flat代表的是当前函数运行耗时,当分析维度是heap,flat代表的是当前函数占用内存信息,但是他们都表示的是当前函数,依次类推。
flat:只包含当前函数的X信息,不包括其调用函数X的信息。flat%:函数自身X所占的总比例。sum%:函数自身累积X占用总比例。cum:函数自身及其调用函数的累计总X。cum%:函数自身及其调用函数的X总比例。
X 根据维度不同代表含义也不同
- 当内存分析时,代表所占内存大小;
- 当CPU分析时,代表所占运行耗时;
2. 排查流程(找出最占内存的函数)
步骤一:使用top排序,步骤二:使用list,查看具体代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
# 使用top -cum,根据累计占用内存排序
(pprof) top -cum
Showing nodes accounting for 11.37MB, 100% of 11.37MB total
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
0 0% 0% 11.37MB 100% main.testPprofHeap.func1
0 0% 0% 11.37MB 100% strings.(*Builder).Grow (inline)
11.37MB 100% 100% 11.37MB 100% strings.(*Builder).grow (inline)
0 0% 100% 11.37MB 100% strings.Repeat
# 使用list,查看具体代码信息;
(pprof) list testPprofHeap
Total: 11.37MB
ROUTINE ======================== main.testPprofHeap.func1 in /Users/liuqh/ProjectItem/GoItem/go-pprof/main.go
0 11.37MB (flat, cum) 100% of Total
. . 31:func testPprofHeap() {
. . 32: go func() {
. . 33: var stringSlice []string
. . 34: for {
. . 35: time.Sleep(time.Second *2)
. 11.37MB 36: repeat := strings.Repeat("hello,world", 50000)
. . 37: stringSlice = append(stringSlice,repeat)
. . 38: fmt.Printf("time:%d length:%d \n",time.Now().Unix(),len(stringSlice))
. . 39: }
. . 40: }()
. . 41:}
|
踩坑:No source information for
在使用list x,报错:No source information for
1
2
3
4
|
(pprof) list testPprofHeap
Total: 11.37MB
No source information for main.testPprofHeap.func1
(pprof) exit
|
解决方法:
1
2
|
# 使用下面格式替换: go tool pprof http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap
➜ go tool pprof compileName http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap
|
compileName:指的是编译后的程序文件
3.3 可视化分析
1. 安装graphviz
1
2
3
4
|
# mac
brew install graphviz
# ubuntu
sudo apt install graphviz
|
更多安装方法:https://graphviz.org/download
2.方式一:web
1
2
|
# 在交互式命令行中输入:web,会自动打开浏览器
(pprof) web
|
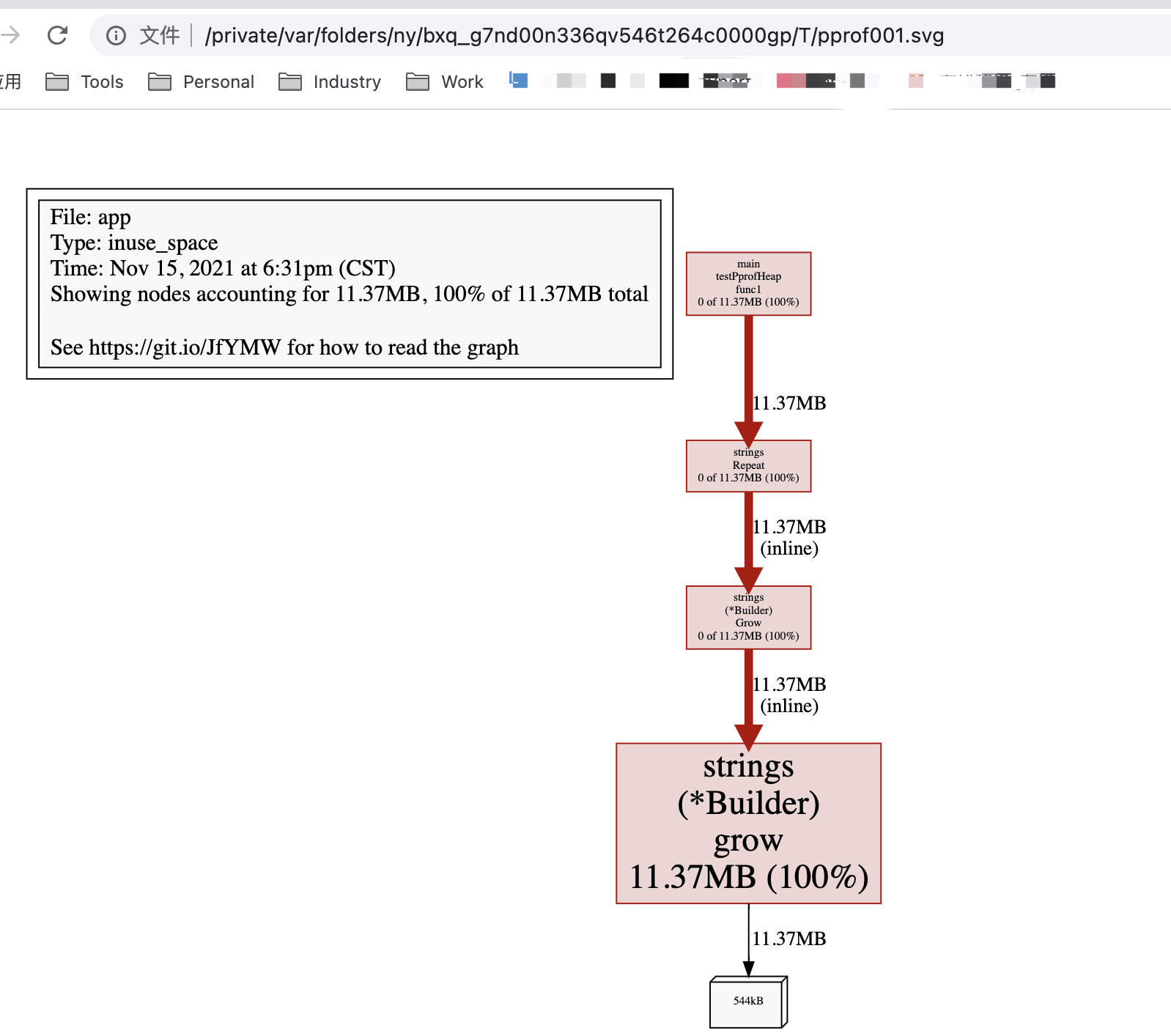
3.方式二:-http :port
1
2
|
# 使用参数 -http :9090,直接在浏览器查询
➜ go tool pprof -http :9090 http://127.0.0.1:6060/debug/pprof/heap
|





